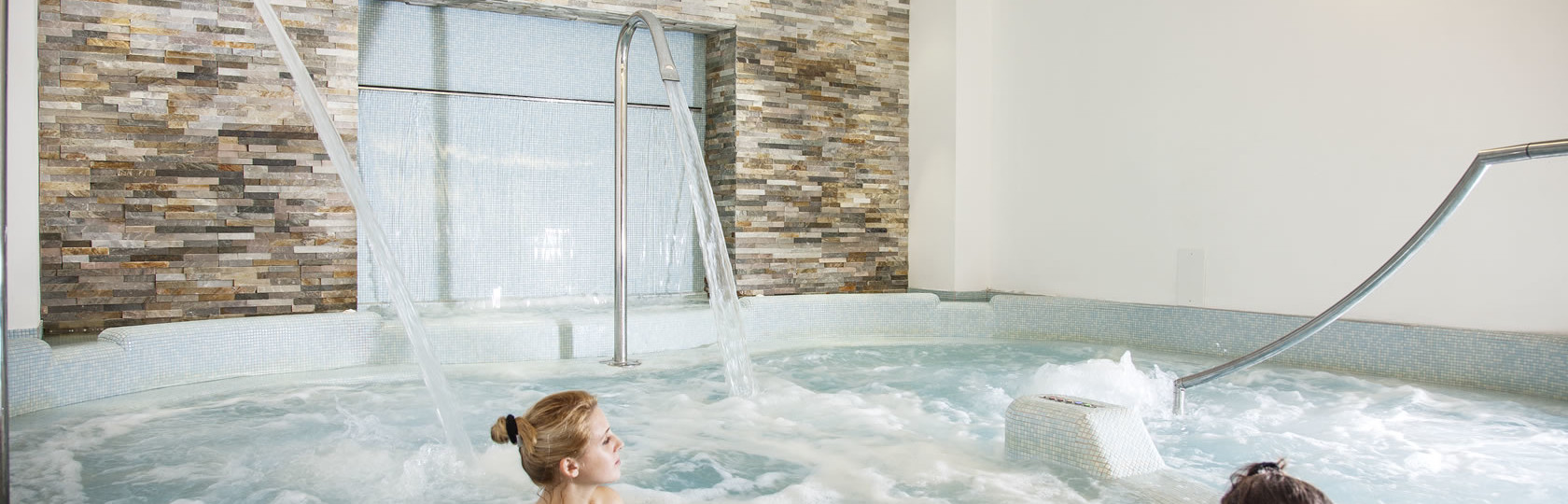
Wellness area bath sanitization system
In order to research innovative sanitization systems for the waters used in the swimming and bathing plants, Terme di Pejo took part in an international cooperation project, financed by the LEADER Project of the European Commission and by the Gruppo di Azione Locale (Local Action Group) of Val di Sole, aimed at developing and experimenting eco-sustainable and biocompatible water sanitization systems and at analyzing the relevant chemical, microbiological and sanitary effects.
A study group named ‘POSEIDON II’ was created with the participation of three European spa facilities, Bad Buchau in Germany, Archena in Spain and Pejo in Italy. The thermal springs of the three spas have different properties as concerns their chemical composition and their therapeutic effects. It was precisely thanks to this difference in thermal springs elements that a new sanitization system could be tested.
Regulations for disinfecting thermal waters are not homogeneous in the three countries: this is allowed in Spain and in Germany under certain circumstances , but it is not allowed in Italy. The process for sanitizing the swimming and wellness facilities is also different in the three countries and the most commonly used products are chlorine and bromine. Their employment has been experimented and tested for years, but it actually can cause problems which should not be underestimated in terms of both technical application and physical effects for bathers.
The study conducted by POSEIDON II analysed the resources the Innowatech Acquadron technology, a system based on the membrane cell electrolysis mechanism, offers to safeguard the microbiological purity and to protect the chemical properties of the mineral and bath waters.
The researches analysed some hydro-chemical parameters and a wide set of microbiological elements (bacteria, ferments, fungi) for quite a long period of time. The clinical aspects were analysed on groups of volunteers who dove into swimming pools sanitized using the new system (Anolyte), and were then compared with the data collected analysing volunteers who had dived into baths sanitized using traditional systems (chlorine and bromine). The collection of subjective data and the analysis of some skin parameters (hydration, sebum measurement, pH, elasticity, TEWL) confirmed that the skin balance was unchanged and demonstrated the absence of negative phenomena even in subjects suffering from dermatologic diseases and allergies or in subjects with hyper-sensitive or reactive skin.